Summary
This paper analyzes data from the alleged measles outbreak of Samoa in 2019, and questions the official narrative that low vaccination rates led to the outbreak and deaths.
Key pieces of data analyzed include trends in mortality of children under the age of 5, historical vaccination coverage and measles cases in Samoa, and the data around vaccination coverage and cases in late 2019 when the outbreak occurred.
By analyzing the above, we observe that in 2019, there was no excess mortality of children under the age of 5, and based on vaccination and cases data, we question the conclusion that low vaccination rates were responsible for an outbreak and the associated deaths.
The mainstream narrative
In 2019, a measles outbreak in Samoa allegedly resulted in over 5600 cases & 83 deaths. It has been argued that low vaccination rate in Samoa led to outbreak.[1]
Several media outlets blamed vaccine hesitancy and low vaccination coverage as the root cause of this tragedy. By and large, the sequence of events reported were as below
In 2018, 2 babies died following measles rubella vaccination. Subsequently, vaccination was suspended and investigation was carried on. [2]
Officials concluded that vaccination was not the cause of deaths. Rather it was a case of human error in administration of vaccine. 2 nurses were found guilty and sentenced to 5 years in prison.[3] [4]
The vaccination program for measles rubella resumed. However, vaccination uptake was low due to the above tragedy. [5] [6]
A measles outbreak occurred in late 2019, leading to over 5,600 cases and 83 deaths. Low vaccination rates were blamed for this tragedy.
Let us now focus on a few observations that call into question the mainstream narrative.
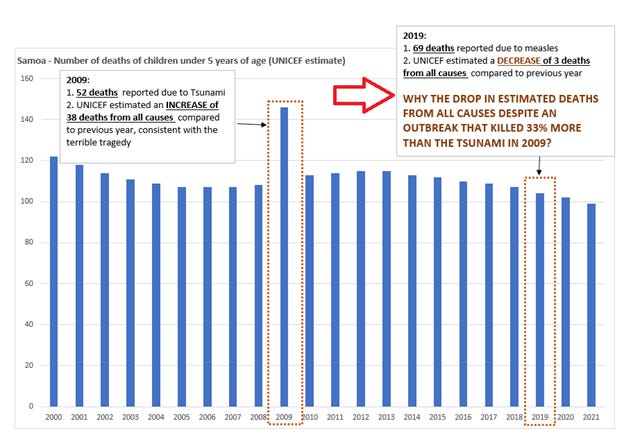
Observation #1: 52 deaths in 2009 Tsunami vs 69 deaths in 2019 measles outbreak: Excess deaths were reported for 2009 but not 2019. How is this possible given that the 2019 outbreak resulted in more deaths?
In 2009, Samoa was hit by a tragic Tsunami. This natural disaster resulted in a loss of over 140 lives, and per the information released by the Government, 52 of these were under the age of 5. [7] UNICEF estimated the death from all causes for children under the age of 5 in 2009, was 38 higher than 2008 (146 vs. 108), clearly implying that the Tsunami played a decisive role in this increase in estimated deaths. [8]
Fast forward to 2019, the media reported 83 deaths from the measles outbreak, and based on information shared by Government of Samoa, at least 69 of these were of children under the age of 5. So 69 deaths from measles in 2019, compared to 52 deaths from Tsunami in 2009. In short, the measles outbreak in 2019 resulted in 33% more deaths compared to the Tsunami in 2009. Despite this fact, UNICEF estimated the death from all causes to be 104 in 2019, compared to 107 in 2018, and 146 in 2009. So UNICEF actually estimated a DECLINE in deaths from all causes in 2019, despite a reported outbreak that caused significantly more deaths than the 2009 tsunami. How is this estimate of decline in deaths consistent with the tragedy of 69 measles deaths, when fewer deaths (52) from the Tsunami tragedy had resulted in a 26% increase estimated deaths from all causes for children under the age of 5? The numbers simply do not reconcile.
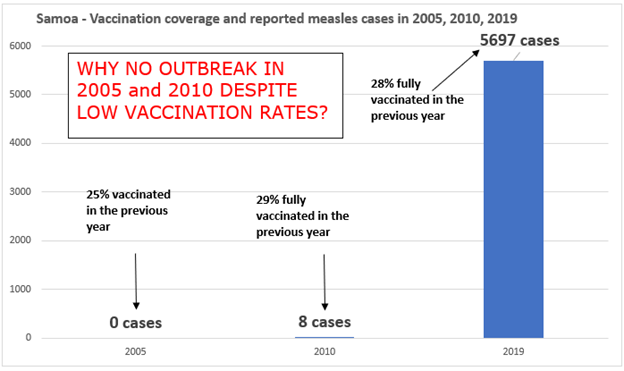
Observation #2: Low vaccination rates in 2004 and 2009 did not lead to measles outbreaks in 2005 and 2010. What changed in 2019?
Why were there 0 measles cases in 2005 when single dose coverage was only 25% in 2004? Similarly, in 2009, when first dose coverage was only 49% and 2nd dose coverage was only 29%, why didn’t measles spread like wildfire in 2010? [9] [10] There were only 8 cases reported in 2010. Why didn’t these 8 cases cause a more widespread outbreak? After all, the vaccination numbers in 2009 were comparable to 2018, and even the coverage in 2010 was well below the herd immunity threshold (61% for 1 dose and 45% for 2 doses)? How can “experts” conclude that low vaccination in 2018 was the cause of the outbreak in 2019, when there was no outbreak in 2005 with even lower vaccination numbers in 2004, and a limited number of cases in 2010 with vaccination numbers from 2009 comparable to 2018? What’s the basis for experts to conclude that low vaccinations lead to outbreaks, if this claim does not hold true at other points in time?
Observation #3: Outbreak declared based on just 7 lab confirmed cases. Non measles cases included in case count. Key pieces of information including vaccine induced measles, vaccine induced measles like illnesses and comparison of vaccinated versus unvaccinated are missing.
Per one of the initial press releases, 7 out of 20 laboratory specimens were confirmed measles cases. Based on such a small number of cases Samoa declared an outbreak. [11]Further, lab testing was no longer recommended after 122 confirmed measles cases. So while the official number of measles cases is around 5,600, only 122 were laboratory confirmed as measles per an update on November 22nd, 2019 following which routine measles testing was no longer recommended[12]. This is an important statistic to keep in mind - given that in tropical countries, there can be measles like illnesses, only a small proportion of which may actually be measles. Per a study from Pahang in Malaysia, only 7% of suspected & notified measles cases over a 5 year period were actually laboratory confirmed as measles.[13] It is important to keep in mind that both Samoa and Pahang have similarities in climate with warm temperatures throughout the year.[14] [15]
Majority of the cases were reported after intensive measles vaccination campaign beginning November 20th. As of November 19th, there were 1174 reported measles cases and 16 measles deaths. Vaccination rate for the year until then works out to approximately 16% of the total population. [16]This implies that after the launch of the vaccination campaign, 4523 cases and 67 deaths were reported. In other words, 79% of the cases and 81% of the deaths were reported after the launch of the intensive measles vaccination campaign on November 20th, the date after which a vast majority of vaccinations took place. [17] We also know that the measles vaccine itself can cause both vaccine strain measles as well as measles like illnesses. [18] [19] [20]How many of the 4523 cases and 67 deaths after the intensive measles vaccination campaign launch on November 20th were actually vaccine induced measles and vaccine induces MLIs (measles like illnesses)?
Further, how many of these cases were vaccinated versus unvaccinated? What was the rate of incidence per 100,000 in these 2 groups? Additionally, what was the rate of all cause mortality in vaccinated versus unvaccinated groups? Surely if low vaccination rates are to be inferred as the cause, this is an important piece of statistic one would rely on to draw this conclusion?
Observation #4: There were reports around vaccine safety and violation of the principle of informed consent. Were uncomfortable questions about vaccine safety and informed consent ignored?
One of the 2 children who died following MMR vaccination in 2018 was allegedly force vaccinated. [21]
Health official acknowledged forced vaccination and stressed importance of informed consent.[22]
The Prime Minister himself noted that many years ago one of his own grandsons lost ability to speak following vaccination. [23]
Prior to the 2018 tragedy, a couple had lost both their babies to MMR vaccination (in 2016 & 2017). They offered to depose before the commission set up to investigate the vaccination deaths, but oddly enough were shut out. [24] [25]
Are the above facts ever shared when discussing the Samoa measles outbreak or the post MMR vaccine deaths that preceded it? What was the inexplicable reason for not investigating 2 other post-MMR vaccine deaths of a distraught couple?
Conclusion
Every death is sad and this paper does not intend to trivialize deaths that occurred in 2019. It does question though if there was excess mortality observed in the under 5 age group that can be attributed to a disease outbreak. Additionally, it does question if low vaccination rates were to be blamed. By analyzing mortality data, vaccination coverage and measles cases history, the paper calls into question the mainstream narrative that low measles vaccination coverage led to a disease outbreak resulting in excess mortality in children below the age of 5 in Samoa in 2019.
[1] https://twitter.com/samoagovt/status/1214429581760819200
[2] https://www.nzherald.co.nz/nz/samoa-has-seized-all-mmr-vaccines-after-deaths-of-two-toddlers/RR6H4PU3CEKJTX4VH7FVBD6YWU/
[3] https://www.samoaobserver.ws/category/samoa/46741
[4] https://www.samoanews.com/baby-deaths-caused-incorrect-vaccination-procedure-samoa-health-ministry-confirms
[5] https://www.rnz.co.nz/international/pacific-news/386249/samoa-mmr-vaccinations-to-resume-on-april-15
[6] https://www.rnz.co.nz/international/pacific-news/398066/no-measles-outbreak-in-samoa-says-health-chief
[7] https://www.preventionweb.net/files/27077_tsunamipublication2wfblanks.pdf
[8] hthttps://data.unicef.org/topic/child-survival/under-five-mortality/
[9] https://immunizationdata.who.int/pages/coverage/mcv.html?CODE=WSM&ANTIGEN=MCV1+MCV2&YEAR=
[10] https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/reported-cases-of-measles?tab=chart&country=~WSM
[11] https://www.facebook.com/samoagovt/posts/pfbid02rFhc6Gk1VFCscsJACHcPEGwRj1Kg1GZDYQJyN5uG6eT7tPxdcBhBRbko3UtpfxhZl
[12] https://www.facebook.com/samoagovt/posts/pfbid028C4Dcsice4xM5KbFfWCuyP65P5cHbdQdVy5H5L1Zr1wshXsuAeZpLmJ1FqcwrFRzl
[13] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35805675/
[14] https://www.pahangtourism.org.my/index.php/about-us/travellers-essentials2/climate
[15] https://www.samoa.travel/samoa-travel-advice/climate-weather
[16] https://www.facebook.com/samoagovt/posts/pfbid0FgB1pzeL6Y7KahbqZ99X9sDTQDqh3Fk2C6ZmC8FRJqjntN4CSr6d63BZfUpDaYU5l
[17] https://www.facebook.com/samoagovt/posts/pfbid0tfbnNM6a122UhYMwJfQh6yBVQKhQr18nJZ4q3xNLhX9SdLMtNy1T9mdvKvHfic8Al
[18] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0031302517303884
[19] https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/19662703812
[20] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK236288/?report=reader
[21] https://www.nzherald.co.nz/nz/samoa-has-seized-all-mmr-vaccines-after-deaths-of-two-toddlers/RR6H4PU3CEKJTX4VH7FVBD6YWU/
[22] https://www.samoaobserver.ws/category/samoa/28260
[23] https://www.nzherald.co.nz/nz/samoa-has-seized-all-mmr-vaccines-after-deaths-of-two-toddlers/RR6H4PU3CEKJTX4VH7FVBD6YWU/
[24] https://www.nzherald.co.nz/nz/nz-samoan-couple-shut-out-of-samoan-inquiry-into-vaccine-deaths-despite-losing-two-children/IWNST2D7UD3AQYDSAF4IZAFDYI/
[25] https://www.nzherald.co.nz/nz/karl-and-christine-laulu-continue-to-grieve-for-two-babies-lost-after-vaccinations-in-samoa/CRPQYGAKDNDBGUCZ27GT5O4EUU/